Teaching in 2024 offers a complex array of challenges and rewards. As educators navigate the evolving landscape of the classroom, understanding the pressures and expectations is paramount. The need for adaptability is clear, with digital learning tools and innovative pedagogies reshaping how teachers connect with and inspire their students.
Focusing on personal well-being is equally critical, ensuring that passion for teaching doesn’t wane in the face of stress and workloads.
The teaching profession continues to transform, spurred by technological advances and shifts in educational philosophy. To thrive, teachers must actively seek professional development opportunities and cultivate supportive networks. Encouraging student success, leveraging digital tools adeptly, and embracing leadership roles are crucial steps toward securing educational success.
- Teachers need to stay adaptable and innovative.
- Professional growth and support networks are essential.
- Navigating digital tools effectively is key to teaching success.

Evolving Educational Trends and Their Impact
- In 2024, educational trends are heavily influenced by technological innovation and student-centric learning models. These trends show a shift towards personalized education plans that cater to individual student needs and pacing.
- Online learning platforms have experienced a surge, offering a plethora of resources and opportunities for students and educators alike, reflecting a landscape where digital literacy is no longer optional for teachers—it’s imperative.
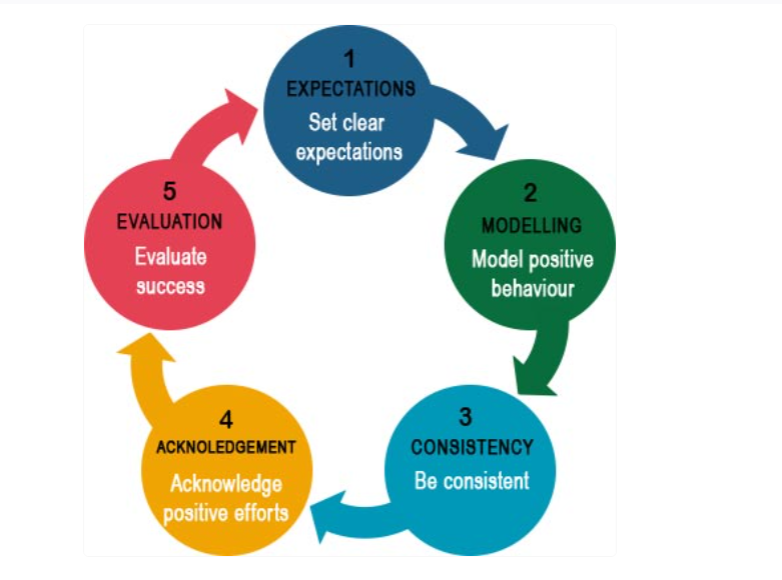
Positive behavioural support (PBS) is a comprehensive, research-based proactive approach to behavioural support that endeavours to generate comprehensive change for students with challenging behaviour. It involves identifying the purpose of challenging behaviour, teaching appropriate alternative responses that serve the same purpose as the challenging behaviour, consistently rewarding positive behaviours and minimising the rewards for challenging behaviour, and minimising the physiological, environmental, and curricular elements that trigger challenging behaviour.
Proven PBS strategies include altering the classroom environment, increasing predictability and scheduling, increasing choice making, adapting the curriculum, appreciating positive behaviours, and teaching replacement skills. Relevant sources for those interested in implementing PBS are presented.
AISL has partnered with a wide array of learning resources for teachers to support them with learning and teaching robotics, programming and AI engaging and accessible.
PBS is grounded in the philosophical and scientific foundations of behaviour analysis, but also draws on and shares the values and methods of prevention science, implementation science, and, more recently, positive psychology. It is underpinned by the philosophy that human beings thrive in predictable spaces where expectations are clear, new skills are taught, and positive behaviours are richly reinforced.
PBS rests on the principle of progressive levels of individualisation to prevent and address challenging behaviour.
Setting clear expectations
Students might present with challenging behaviours because the expected classroom behaviours have not been explicitly stated or taught. Students can be confused about what is expected of them, and this may be even more true for students with disabilities.
Clear visual cues through posters or pictures and utilising inclusive language helps students understand what behaviours are expected of them in the classroom.
Teachers can direct students to these expectations frequently, consistently apply them, and acknowledge students who have presented with behaviours which align with these expectations.
Teachers can also identify those students who may need more support to learn how to display the expected behaviours in the classroom. Teachers who have established expectations reduce stress in the classroom as students are aware of what they are required to do. Schools should invest time in teaching expectations early and often during the school term. More time invested in teaching expectations can dramatically reduce incidence of challenging behaviours in the school. Setting clear guidelines and expectations, and modelling these behaviours during planned lessons, not only encourages those behaviours, but reinforces their practice over time.